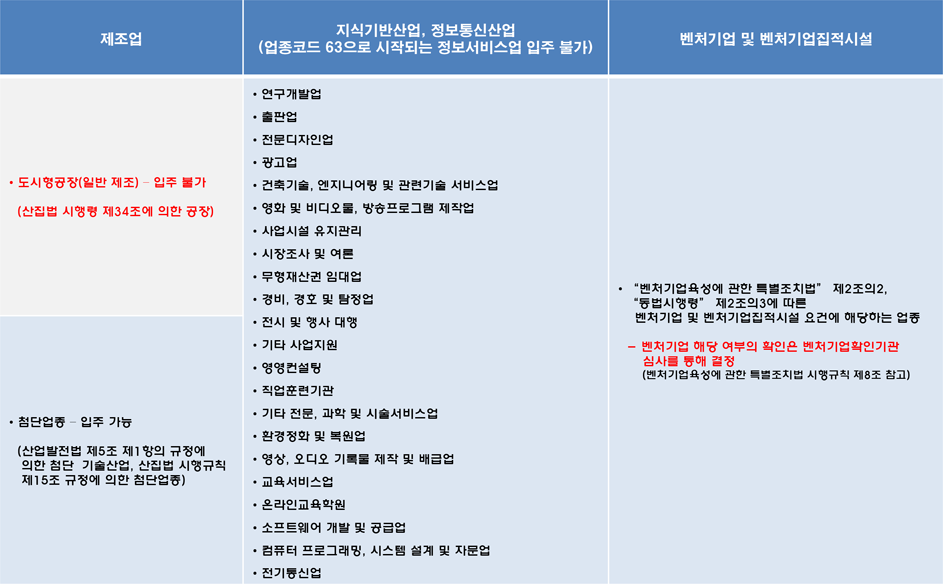
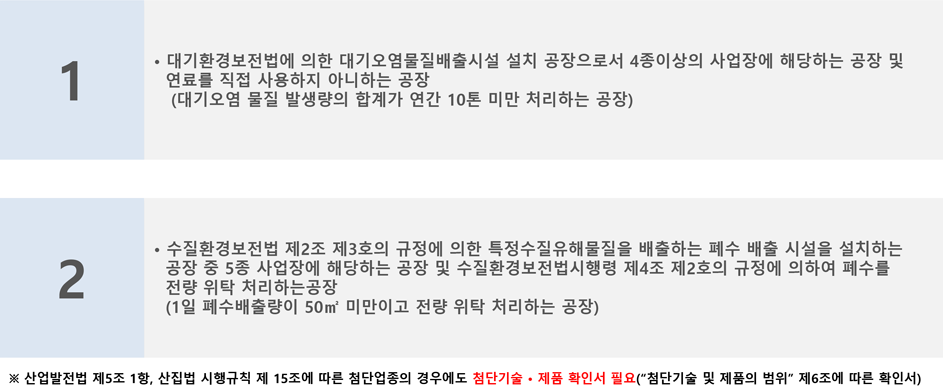
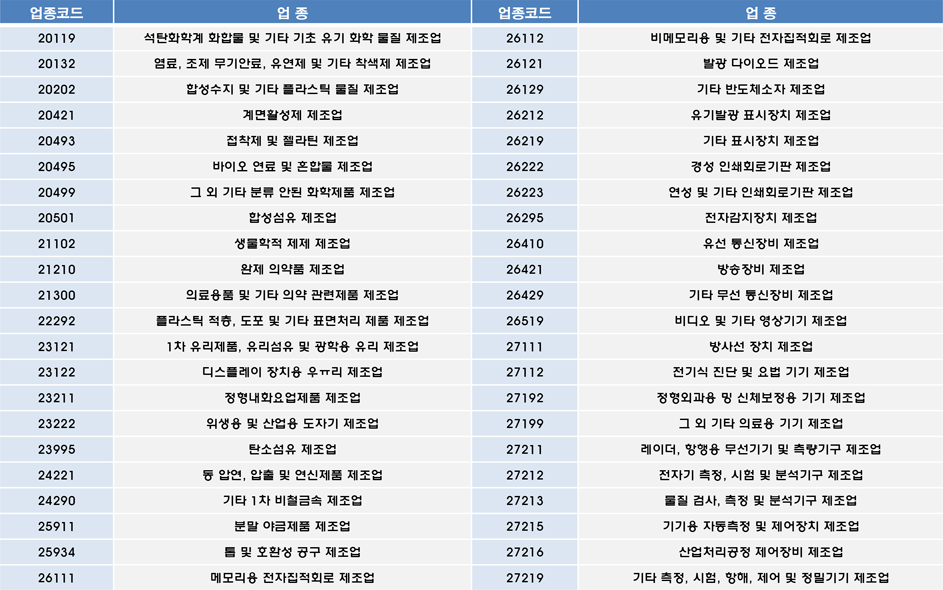
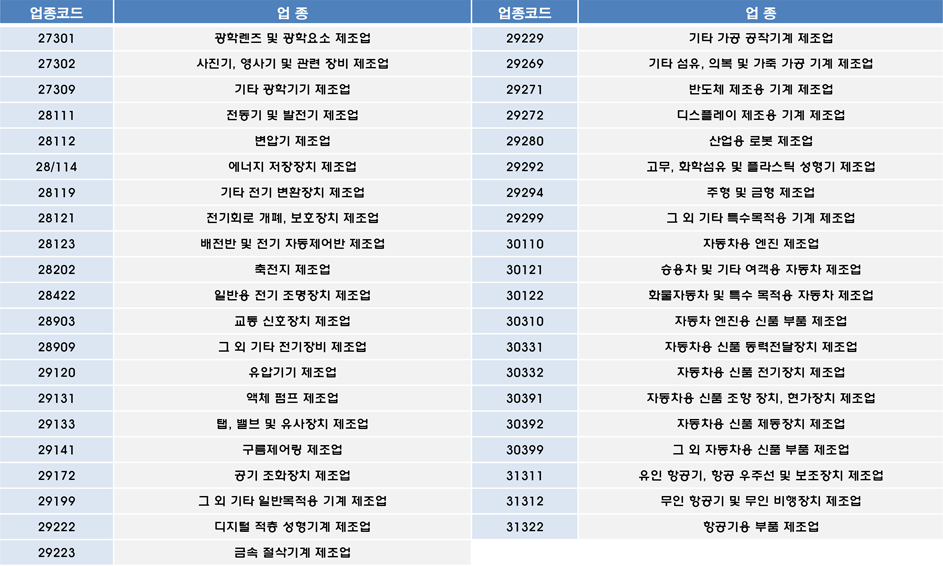
Shhhh... Listen! Do You Hear The Sound Of Compliance Officer Definitio…
페이지 정보

본문
 Introduction:
Introduction:Shares are an essential component of a company's capital structure. They represent ownership interests in the company and offer investors a stake in its profit and decision-making. However, there are distinct differences between outstanding shares and issued shares, which this study aims to explore. By understanding these differences, investors and stakeholders can make informed decisions regarding their investment strategies.
Definition of Outstanding and Issued Shares:
Outstanding shares refer to the total number of shares held by shareholders, including both institutional and individual investors. If you beloved this write-up and you would like to get a lot more details regarding loan loss provision accounting kindly go to our internet site. These shares represent the ownership interest in a company and are crucial in determining voting rights, dividends, and earnings per share. On the other hand, issued shares refer to the shares that a company has actually issued to shareholders, whether they are currently held by investors or being held as treasury stock.
Differences between Outstanding and Issued Shares:
1. Shareholder Voting Rights:
Outstanding shares play a crucial role in determining the voting rights of shareholders. Each outstanding share typically entitles the holder to one vote in major corporate decisions, such as electing the board of directors or approving mergers and acquisitions. Issued shares, however, may include both voting and non-voting shares, which can impact the shareholders' influence on decision-making processes.
2. Dividend Distribution:
Outstanding shares are also fundamental in determining the per-share dividend distribution among shareholders. Dividends are usually paid on a per-share basis, and the total number of outstanding shares directly affects the distribution amount to each shareholder. Issued shares, meanwhile, may include shares held as treasury stock, which do not entitle the holder to receive dividends until they are reissued.
3. Earnings per Share:
Earnings per share (EPS) is a key financial metric used to evaluate a company's profitability and shareholder value. It is calculated by dividing the company's net income by the weighted average number of outstanding shares. The distinction between outstanding and issued shares is crucial in accurately calculating EPS, as only outstanding shares that are actively traded on the market are considered in the calculation.
4. Stock Dilution:
Issued shares can contribute to stock dilution, which occurs when a company issues additional shares, thereby reducing the ownership percentage and earnings per share of existing shareholders. Outstanding shares, however, reflect the total ownership interest and can provide a clearer picture of the dilution effect on existing shareholders.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding the differences between outstanding and issued shares is essential for investors and stakeholders. Outstanding shares represent the total ownership interest in a company, while issued shares refer to the shares that have been actually issued to shareholders. These differences impact voting rights, dividend distribution, earnings per share, and potential stock dilution. By analyzing these distinctions, investors can make informed decisions and assess their ownership status accurately.
- 이전글Why When Is Honeydew Melon In Season Is No Friend To Small Business 24.04.08
- 다음글etodolac è in vendita senza prescrizione in Italia Consulta il costo di lodine con prescrizione a Messina 24.04.08
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.